Day 1: Enterprise Agent Architecture - Building Production-Ready AI Agents
The Problem We're Solving
When you use apps like Netflix, Uber, or Discord, you expect them to work perfectly every time. Behind the scenes, these companies run millions of AI agents that handle user requests, process data, and make decisions. But what happens when something goes wrong?
Most student projects crash when they encounter errors, lose data when restarted, or expose sensitive information through poor security. In the real world, a single failed agent could cost thousands of dollars or leave users stranded. This lesson teaches you to build agents with enterprise-level reliability - the same patterns used by major tech companies.
What We're Building Today
Today we'll construct a production-grade AI agent with enterprise-level reliability. Think of how Netflix handles millions of requests without crashing - that's the robustness we're building into our agent.
Key Components:
Secure agent lifecycle management
Encrypted state persistence
Comprehensive error handling
Professional CLI interface with logging
Why This Matters in Real Systems
When Stripe processes payments or Uber matches rides, their agents must handle failures gracefully. A single crashed agent could lose thousands of dollars or strand users. Enterprise architecture prevents these disasters.
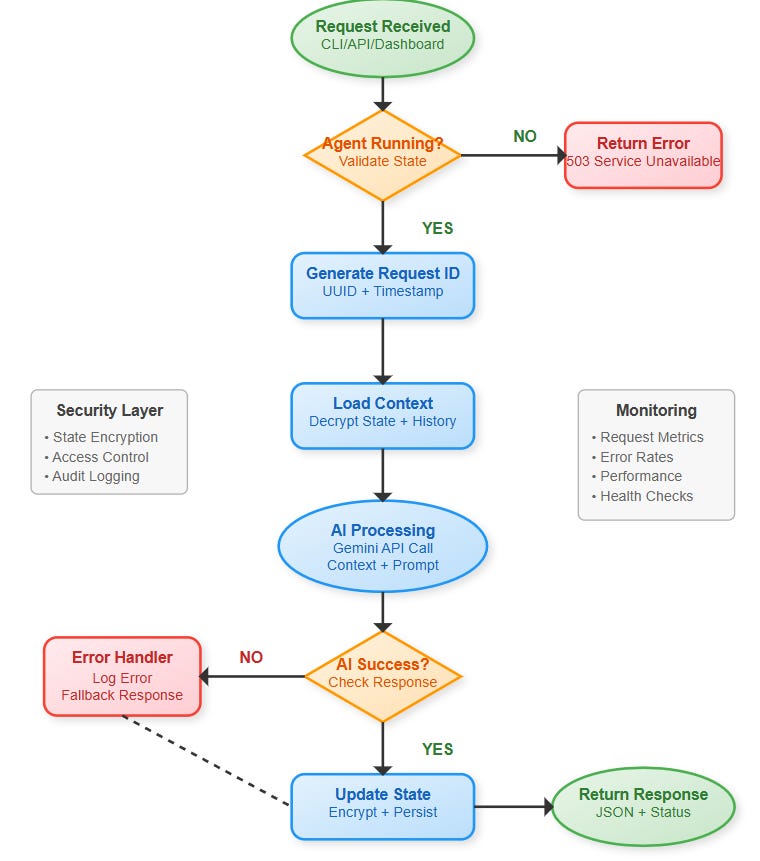
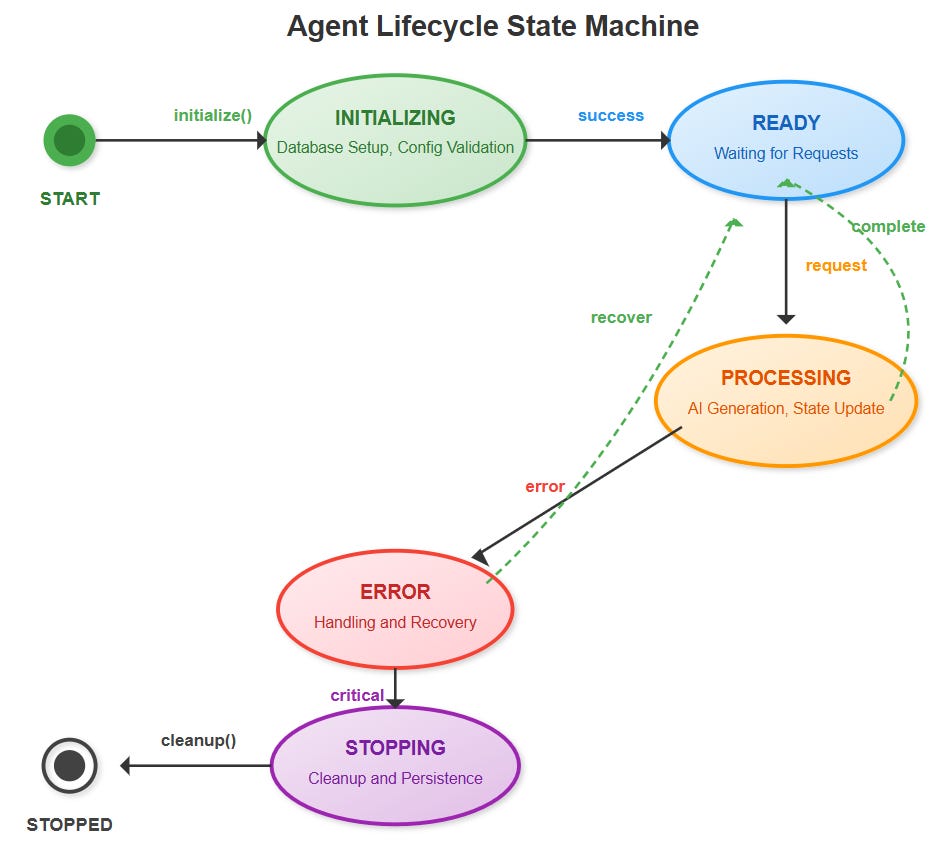
Core Concept: Agent Lifecycle Management
Every production agent follows three critical phases:
Initialization: Secure startup with configuration validation and resource allocation. Like booting a server - everything must be verified before accepting work.
Execution: Processing requests while maintaining state consistency. The agent handles concurrent operations while preserving data integrity.
Cleanup: Graceful shutdown with state persistence and resource release. No data loss, no hanging processes.
State Management Architecture
Real agents need persistent memory across restarts. We implement:
Encrypted Storage: All state data encrypted at rest using AES-256. Even if someone accesses the database, they can't read sensitive information.
Recovery Strategies: Automatic state restoration after failures. The agent picks up exactly where it left off.
Persistence Patterns: Regular checkpoints ensure minimal data loss during unexpected shutdowns.
Error Handling Strategy
Production systems fail - networks drop, APIs timeout, memory fills up. Our agent handles these gracefully:
Logging Levels: Structured logs capture everything from debug info to critical alerts. Engineers can trace exactly what happened during failures.
Alerting Systems: Automatic notifications when errors exceed thresholds. Teams know about problems before customers complain.
Graceful Degradation: When AI services fail, the agent continues with reduced functionality instead of crashing completely.
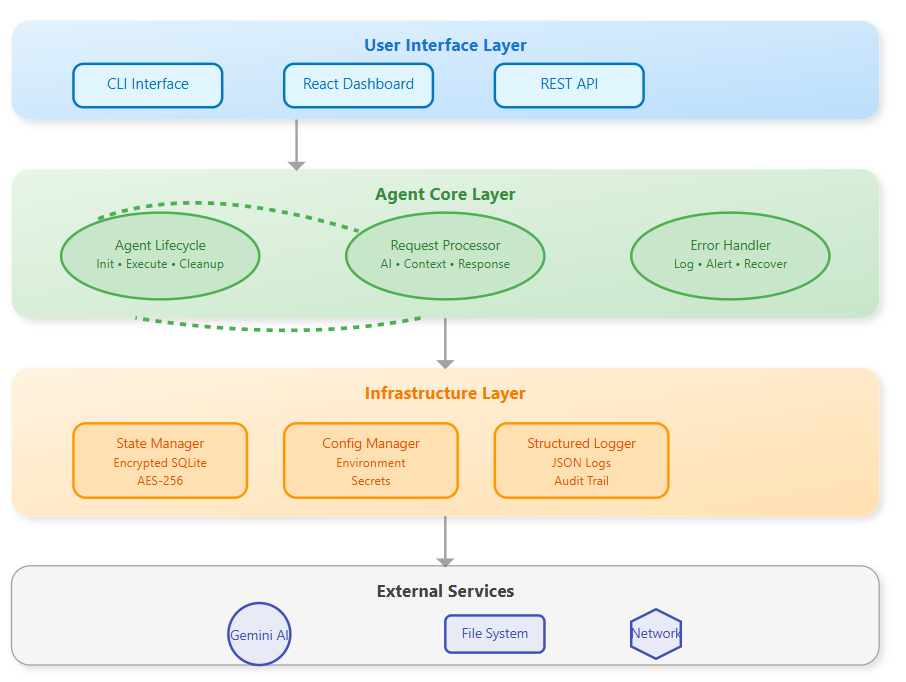
Component Architecture
Our agent consists of five core modules:
Agent Core: Main orchestration engine managing lifecycle and state
Memory Manager: Handles encrypted storage and retrieval
Error Handler: Catches, logs, and recovers from failures
CLI Interface: Professional command-line interface for operations
Config Manager: Secure configuration and environment management
Implementation Highlights
CLI Design: Professional interface supporting commands like agent start, agent status, and agent logs - similar to Docker or Kubernetes CLIs.
Configuration: Environment-based config supporting development, staging, and production settings. Secrets stored securely, never in code.
Monitoring: Real-time metrics and health checks enabling proactive maintenance.
Real-World Context
This architecture mirrors patterns used by:
Slack bots handling millions of messages daily
GitHub Actions running CI/CD workflows reliably
AWS Lambda processing serverless functions at scale
Success Criteria
By lesson end, you'll have:
A production-ready agent that starts, processes, and stops cleanly
Encrypted state that survives restarts
Comprehensive logging and error handling
Professional CLI interface for operations
Assignment: Build Your Production Agent
Task: Extend the base agent with custom functionality and demonstrate production readiness.
Requirements:
Add a new CLI command
agent metricsthat shows request statisticsImplement a health check endpoint that validates all system components
Create a custom error scenario and demonstrate graceful recovery
Add request rate limiting to prevent system overload
Deliverables:
Modified CLI with metrics command
Health check implementation with component validation
Documentation of error scenario and recovery
Rate limiting demonstration with before/after performance
Solution Hints
Metrics Implementation:
python
# Add to AgentCore.get_metrics()
return {
'requests_per_minute': calculate_rpm(),
'error_rate': errors / total_requests,
'avg_response_time': sum(times) / len(times),
'uptime': current_time - start_time
}Health Check Strategy:
Test database connectivity
Verify API key validity
Check disk space for logs
Validate encryption system
Rate Limiting Approach:
Implement token bucket algorithm
Track requests per client/session
Return 429 status when limit exceeded
Log rate limit violations
Implementation Guide
GitHub Link:
https://github.com/sysdr/AI-Agent-Mastery/tree/main/day1/enterprise_agentPrerequisites
Before starting, ensure you have:
Python 3.11 or higher
Node.js 18 or higher
Gemini API key (get from makersuite.google.com)
Basic understanding of command line operations
Step 1: Project Structure Setup
Create the foundation for your enterprise agent:
bash
mkdir enterprise_agent && cd enterprise_agent
mkdir -p backend/src/{agent,utils,config}
mkdir -p frontend/src/{components,services}
mkdir -p tests/{unit,integration}
mkdir -p dockerStep 2: Backend Core Implementation
Agent Core Development
The heart of your agent lives in backend/src/agent/core.py. This file implements:
Lifecycle Management: Proper initialization, execution, and cleanup
State Persistence: Encrypted storage with automatic recovery
Error Handling: Graceful degradation and comprehensive logging
Key methods to implement:
initialize(): Set up database, load state, validate configurationprocess_request(): Handle user inputs with context managementcleanup(): Graceful shutdown with state preservation
Security Layer
Create backend/src/utils/encryption.py for data protection:
python
from cryptography.fernet import Fernet
class EncryptionManager:
def __init__(self):
self.cipher_suite = Fernet(settings.encryption_key)
def encrypt(self, data: str) -> str:
return self.cipher_suite.encrypt(data.encode()).decode()
def decrypt(self, encrypted_data: str) -> str:
return self.cipher_suite.decrypt(encrypted_data.encode()).decode()Professional CLI Interface
Build backend/src/cli.py with these commands:
start: Initialize and launch the agentstatus: Display health metrics and system statechat: Interactive communication with the agentlogs: View recent activity and errorsstop: Graceful shutdown with cleanup
Step 3: Frontend Dashboard
React Application Setup
Your dashboard provides real-time monitoring and interaction capabilities. Key components:
Dashboard.js: Main interface showing:
Agent status and health indicators
Real-time request metrics and charts
Interactive chat interface
System information panel
API Service: Handles backend communication with error handling and timeouts.
User Experience Design
The dashboard should feel professional and responsive:
Clean, modern interface using Material-UI
Real-time updates every 5 seconds
Clear status indicators (healthy/unhealthy)
Intuitive chat interface with message history
Step 4: Configuration and Security
Environment Management
Create .env file for secure configuration:
bash
AGENT_ENV=development
GEMINI_API_KEY=your-api-key-here
ENCRYPTION_KEY=auto-generated
LOG_LEVEL=INFONever commit sensitive data to version control. Use environment variables for all secrets.
Database Setup
Your agent uses SQLite with encryption for state storage:
Automatic table creation on first run
Encrypted data storage using AES-256
Recovery mechanisms for corrupted states
Step 5: Testing and Validation
Unit Testing
Test core functionality in isolation:
bash
cd tests
python -m pytest unit/ -vFocus on testing:
Agent initialization scenarios
Request processing with various inputs
Error handling and recovery
State persistence and encryption
Integration Testing
Verify end-to-end functionality:
API endpoint responses
Database operations
CLI command execution
Frontend-backend communication
Step 6: Build and Deployment
Local Development
Start your development environment:
bash
# Backend (Terminal 1)
cd backend/src
python -m uvicorn api:app --reload --port 8000
# Frontend (Terminal 2)
cd frontend
npm startDocker Deployment
For production-like testing:
bash
docker-compose up --buildThis creates isolated containers for both frontend and backend services.
Step 7: Performance Verification
Functional Testing
Verify your agent works correctly:
bash
cd backend/src
# Test complete lifecycle
python -m cli start
python -m cli status
python -m cli chat "Test message"
python -m cli logs
python -m cli stopLoad Testing
Use tools like curl or Postman to test multiple concurrent requests:
bash
# Test API response time
time curl -X POST http://localhost:8000/chat \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"message": "Performance test"}'Security Validation
Verify encryption is working:
python
# Test encryption functionality
from utils.encryption import EncryptionManager
em = EncryptionManager()
test_data = "sensitive information"
encrypted = em.encrypt(test_data)
decrypted = em.decrypt(encrypted)
print(f"Encryption working: {test_data == decrypted}")Troubleshooting Common Issues
Agent won't start:
Check API key configuration
Verify port 8000 isn't in use
Review logs for specific errors
Frontend connection problems:
Confirm backend is running on port 8000
Check browser console for CORS errors
Verify API endpoints are accessible
Database errors:
Ensure write permissions in data directory
Reset database by deleting
agent_state.dbCheck disk space availability
Next Steps
Tomorrow we'll add secure memory systems with conversation compression and PII detection - the foundation for handling sensitive data in production environments.
The patterns learned today scale from single agents to distributed systems handling millions of requests. Master these fundamentals, and you're ready for enterprise AI engineering.